
Oakover East
The Oakover East Project is located between 40km and 80km to the south of the operating Woodie Woodie manganese mine in the Pilbara region of Western Australia.
The project consists of both 100% owned and Carawine JV tenure, is prospective for manganese, copper and iron with primary focus on the Wandanya Prospect (BCA 100%) and Fig Tree Prospect (BCA 75%).
Background
Previous exploration on the Oakover East tenements has concentrated on extensive outcropping manganese at Fig Tree associated along the contact between the Carawine Dolomite and the overlying Pinjin Chert.
At Wandanya the high-grade manganese and iron appear to be related to a particular stratagraphic horizon but has similarities in terms of grade and mineralogy to hydrothermal mineralisation at Woodie Woodie.
The Fig Tree region has been the subject of previous aerial and surface geophysical surveys, mapping, rock chip sampling and RC drill testing which has provided a substantial high-quality dataset to assist in target evaluation and ranking.
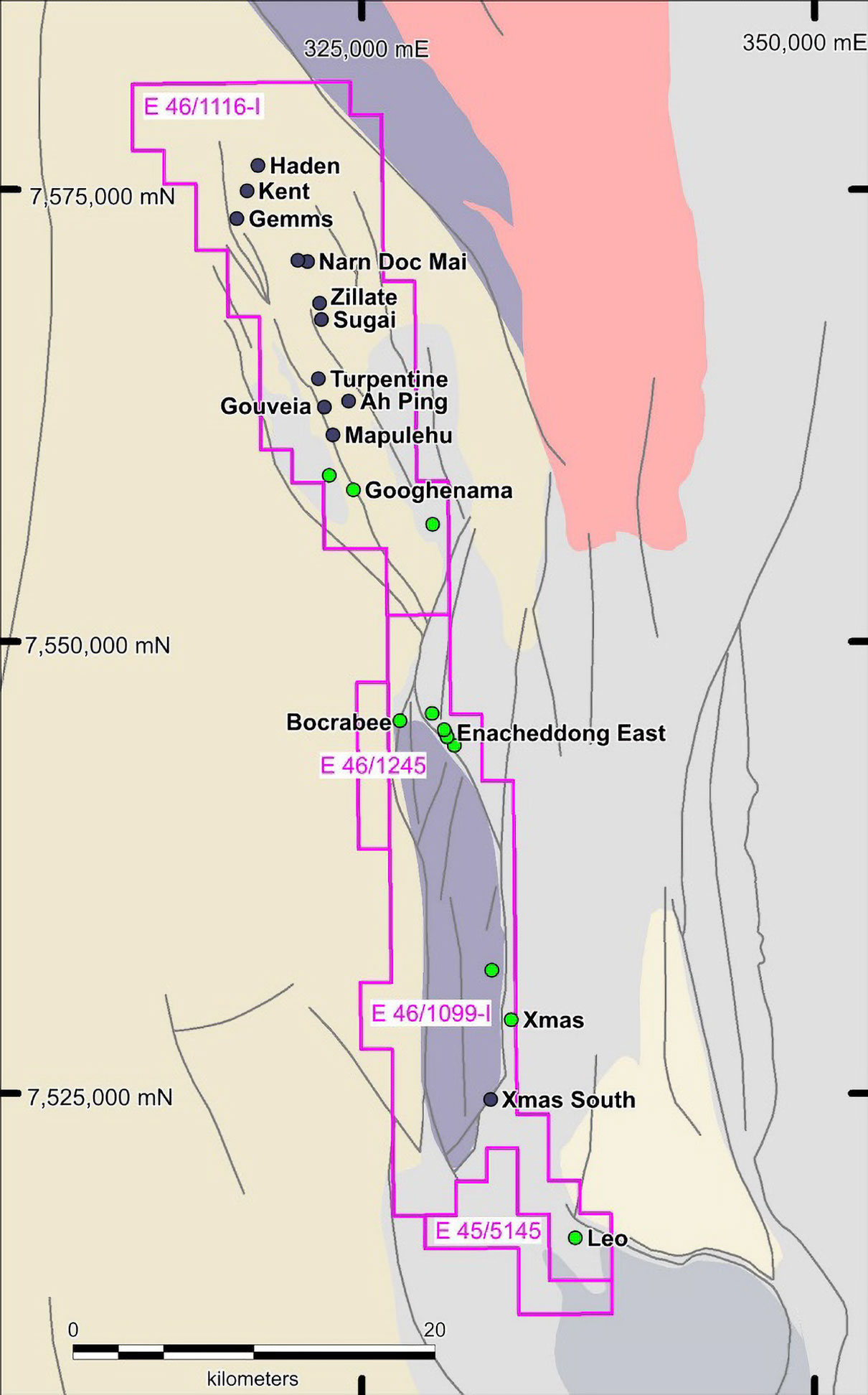
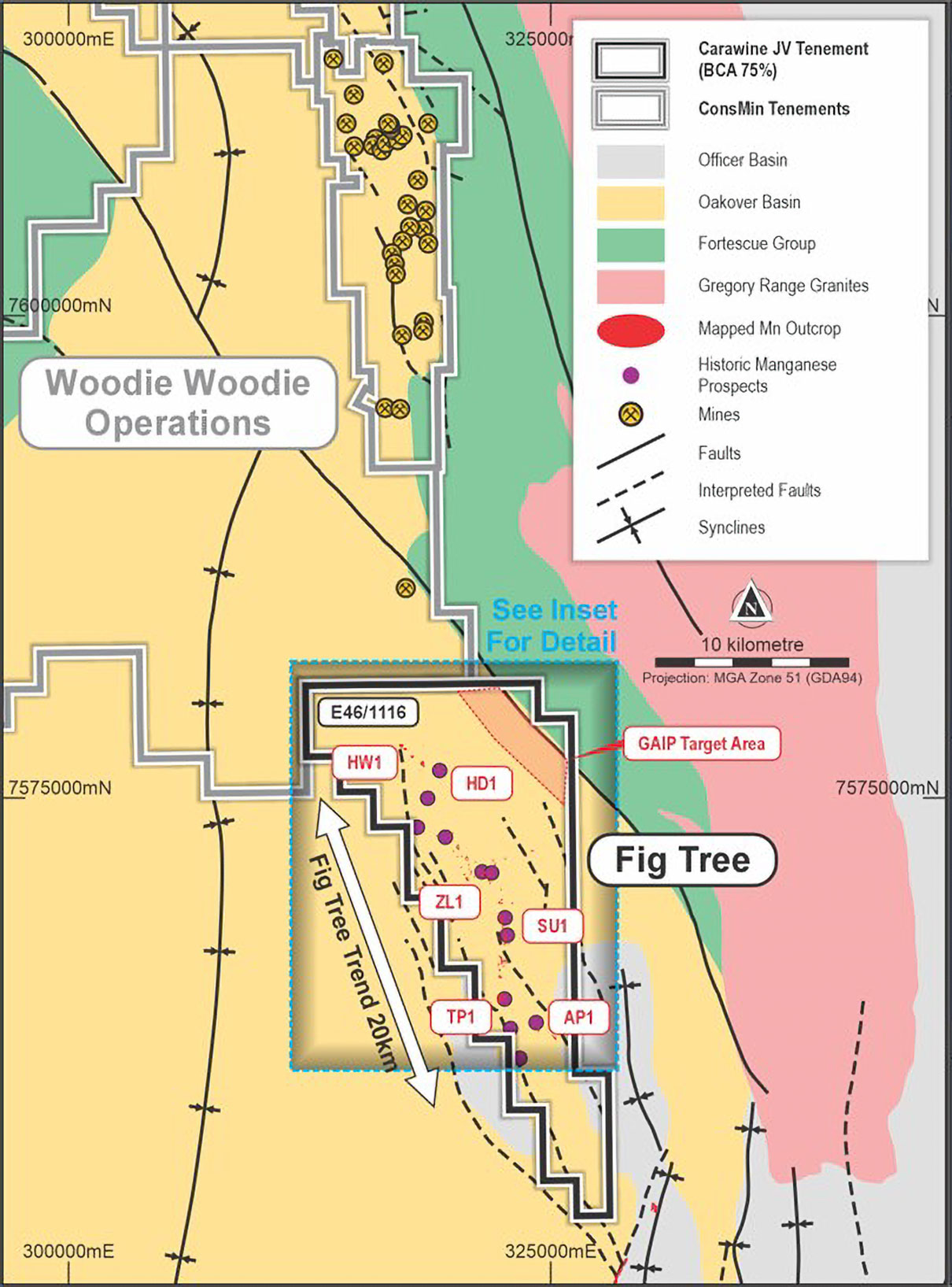
Fig Tree Project
The Fig Tree Manganese Trend comprises a string of prospects with potential for high-grade, hydrothermal style manganese mineralisation and being located only 35km from the Woodie Woodie Operations, has a similar geological setting with previous drilling successfully identifying the prospective manganese corridor.
Black Canyon has leveraged off the high-quality historic exploration dataset that covers the project to carefully review the geological and more importantly the structural setting of the known manganese prospect and to generate new targets for evaluation and drill testing.
The Woodie Woodie operation has a long history of discovering and developing multiple small but high value manganese mineral resources. More than 30 pits have been developed at Woodie Woodie ranging from 0.2Mt to 10Mt with an average size of 0.5Mt1. The strategy for Black Canyon is to explore the multiple discrete known zones of manganese mineralisation and new targets that may develop into mineral resources with the application of ground geophysics and follow-up drill testing.
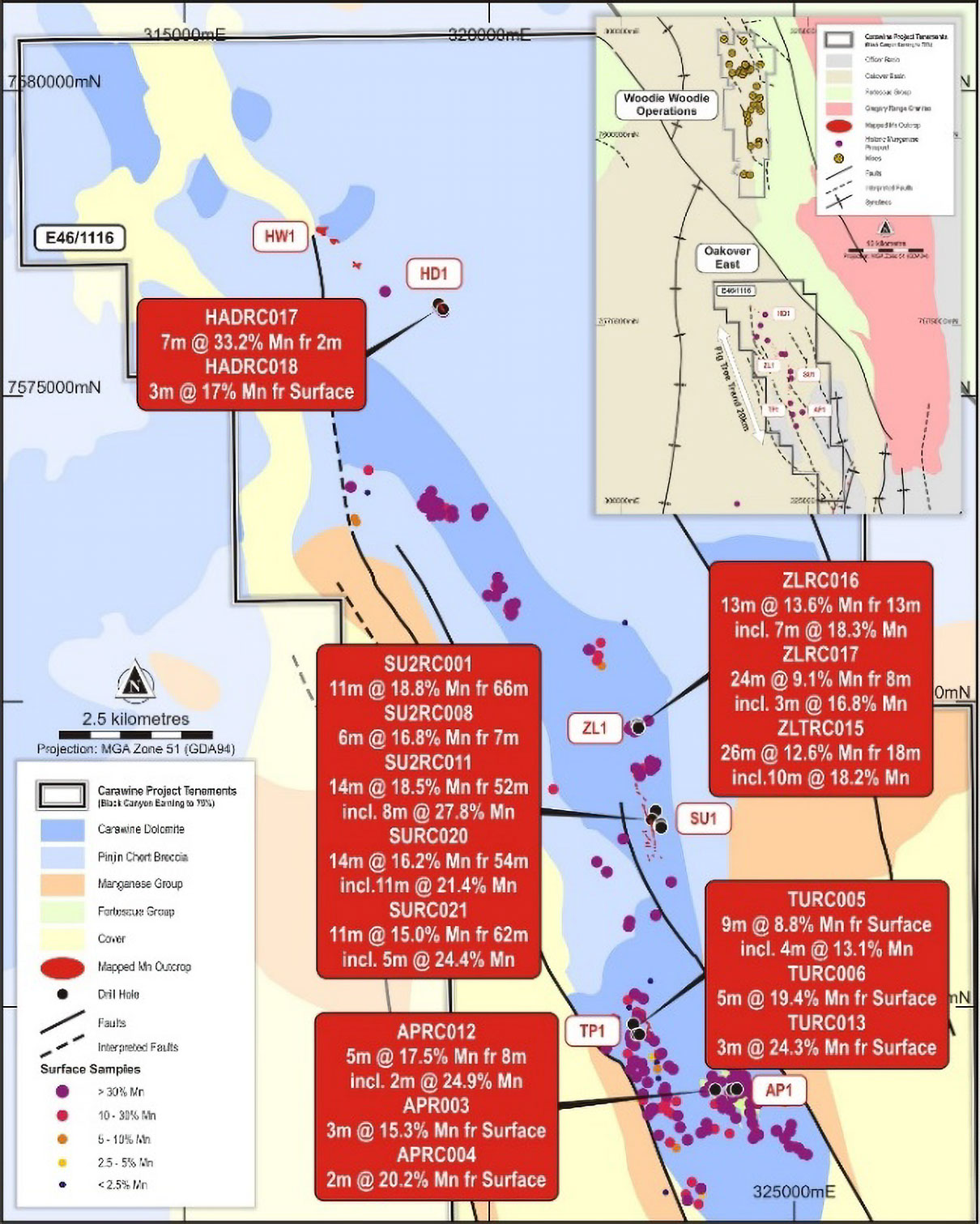
Surface manganese mineralisation was observed along a strike of 1,200m between the SU1 and ZL1 prospects, where previous down dip drilling intersected significant high-grade intervals, including:
- 11m @ 18.8% Mn from 66m (SU2RC001)
- 6m @ 16.8% Mn from 7m (SU2RC008)
- 14m @ 18.5% Mn from 52m including 8m @ 27.8% Mn (SU2RC011)
- 14m @ 16.2% Mn from 54m including 9m @ 21.4% Mn (SURC020)
- 11m @ 15.0% Mn from 62m including 5m @ 24.4% Mn (SURC021)
- 13m @ 13.6% Mn from 13m including 7m @ 18.3% Mn (ZLRC016)
- 26m @ 12.6% Mn from 18m including 10m @ 18.2% Mn (ZLTRC015)
High grade mineralisation was previously sampled and drilled at the HD1 Prospect. The outcrop is 170m long with a width ranging from 10m to 20m. A structurally controlled corridor from the HD1 prospect has been mapped for approximately 2,500m to the NW with three other manganese enriched outcrops also identified. A single rock chip sample was previously taken at one of the three prospects that returned an assay of 34.2% Mn (PM102265) which supports the grade potential of the additional targets. Significant previous drill results from HD1 include:
- 7m @ 33.2% Mn from 2m (HADRC017)
- 3m @ 17.0% Mn from surface (HADRC018)
Elsewhere at the Gemms, and Narn Doc Mai Prospects, numerous rock chip samples grading >50% Mn were returned that require follow up in future programs.
- S. A. Jones (2017): Geology and geochemistry of fault-hosted hydrothermal and sedimentary manganese deposits in the Oakover Basin, east Pilbara, Western Australia, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, DOI: 10.1080/08120099.2017.1272492 ↩︎